1. 기사 요약
- EMA에서 희귀 의약품으로 지정
- 섬유화를 억제하는 글루카곤, 인슐린 분비 및 식욕억제를 돕는 GLP-1, 인슐린 분비 및 항염증 작용의 GIP를 동시에 타깃 하는 삼중 작용제
- FDA, EMA로 부터 "원발 담즙성 담관염, 원발 경화성 담관염, 특발성 폐섬유증으로 총 6건 희귀약품으로 지정
2. HM15211 product
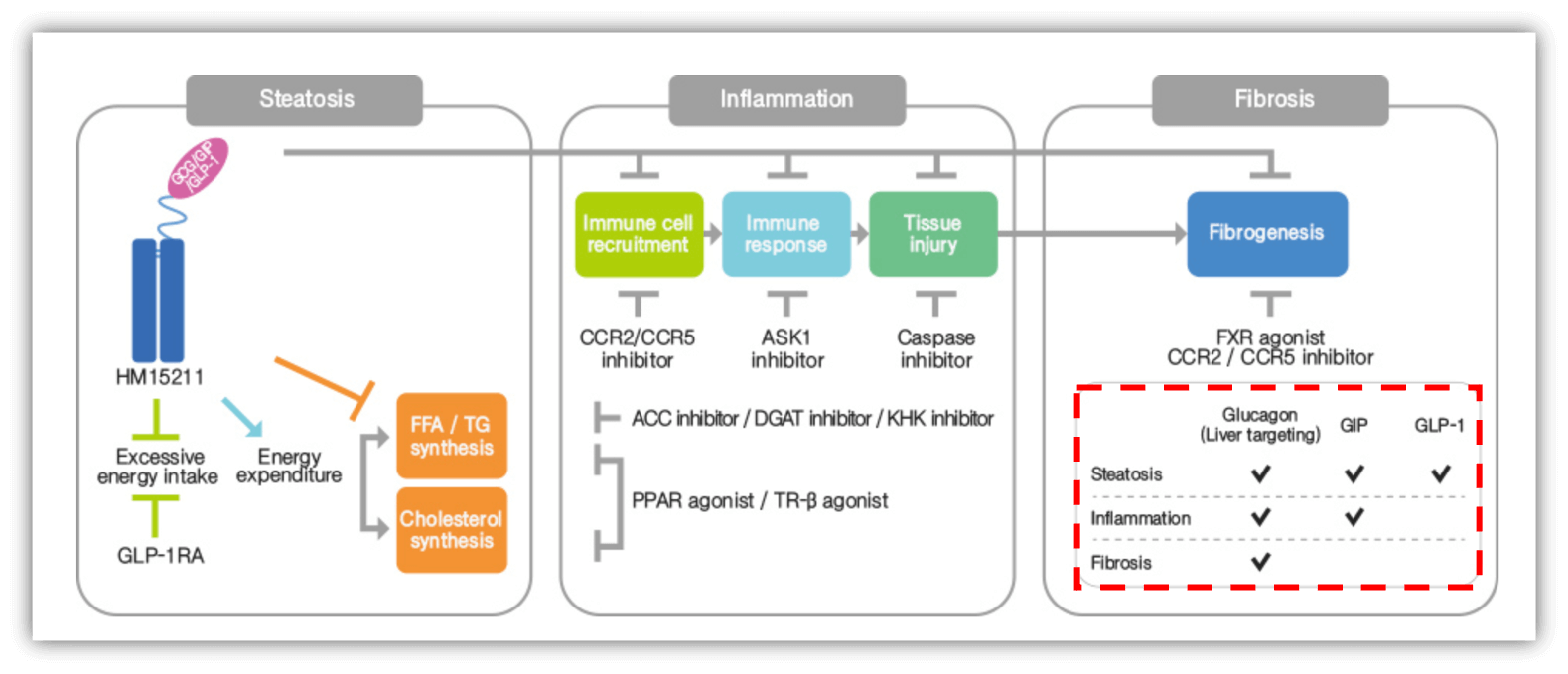
- Molecular Mechanism
- Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide Receptor (GIPR) Agonists
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
- Glucagon Receptor (GCGR) Agonists
- Cellular Mechanism
- Signal Transduction Modulators
- Product Category
- Fc fusion proteins
- Polypeptides, from 41 AA
- Prescription/Designation Type
- Fast Track Designation
- Orphan Drug Designation
HM15211 (LAPS Triple Agonist)
3. 신문 기사
a. [656-P: Antifibrotic Potential of a Novel Long-Acting Glucagon/GIP/GLP-1 Triple Agonist (HM15211) in Preclinical Models of Fibrosis (01 June 2021)]
Fibrosis due to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) remains a major cause of liver-related mortality. Since complex biological pathways are involved in fibrosis progression, multi-disciplinary therapeutic approaches should be required to effectively deliver treatment effects on fibrosis. For this purpose, we developed a novel long-acting Glucagon/GIP/GLP-1 triple agonist, HM15211.
Here, we evaluated the anti-fibrotic effect of HM15211 in various animal models of fibrosis, and investigated underlying mechanism in vitro. Mice fed with AMLN diet were concomitantly treated with thioacetamide (AMLN/TAA mice) for 16 weeks, and HM15211 was administered during last 8 weeks. HM15211 treatment significantly reduced hepatic (-53.9, -41.4 and -51.9 % vs. vehicle for α-SMA, TIMP-1 and collagen1a1 expression) and blood (-49.3, -48.0 and -49.1% vs. vehicle for TIMP-1, PIIINP and hyaluronic acid level) surrogate markers for fibrosis.
HM15211 treatment was also associated with significant reduction in hepatic hydroxyproline (-53.1% vs. Veh) and sirius red positive area (-70.6% vs. Veh) in AMLN/TAA mice. Next, anti-fibrotic effect of HM15211 was further evaluated in choline-deficient and high fat diet (CD-HFD) mice. Strikingly, greater reduction in hepatic hydroxyproline and collagen contents (-4.2, -10.0, -31.2% vs. vehicle for acylated GLP-1, acylated GLP-1/GIP, HM15211) was observed compared to acylated GLP-1 or acylated GLP-1/GIP in CD-HFD mice.
Additional in vitro studies in LX2 cell and rat primary hepatic stellate cell (HSC) unveiled that HM15211 could negatively affect multiple steps of TGF-β signaling in HSC. Based on these results, HM15211 may be a novel therapeutic option for liver fibrosis in addition to NASH itself. Hence, related mechanistic studies further highlight direct inhibitory effect of HM15211 on HSC activation. On-going human efficacy study will assess the clinical relevance of these findings.
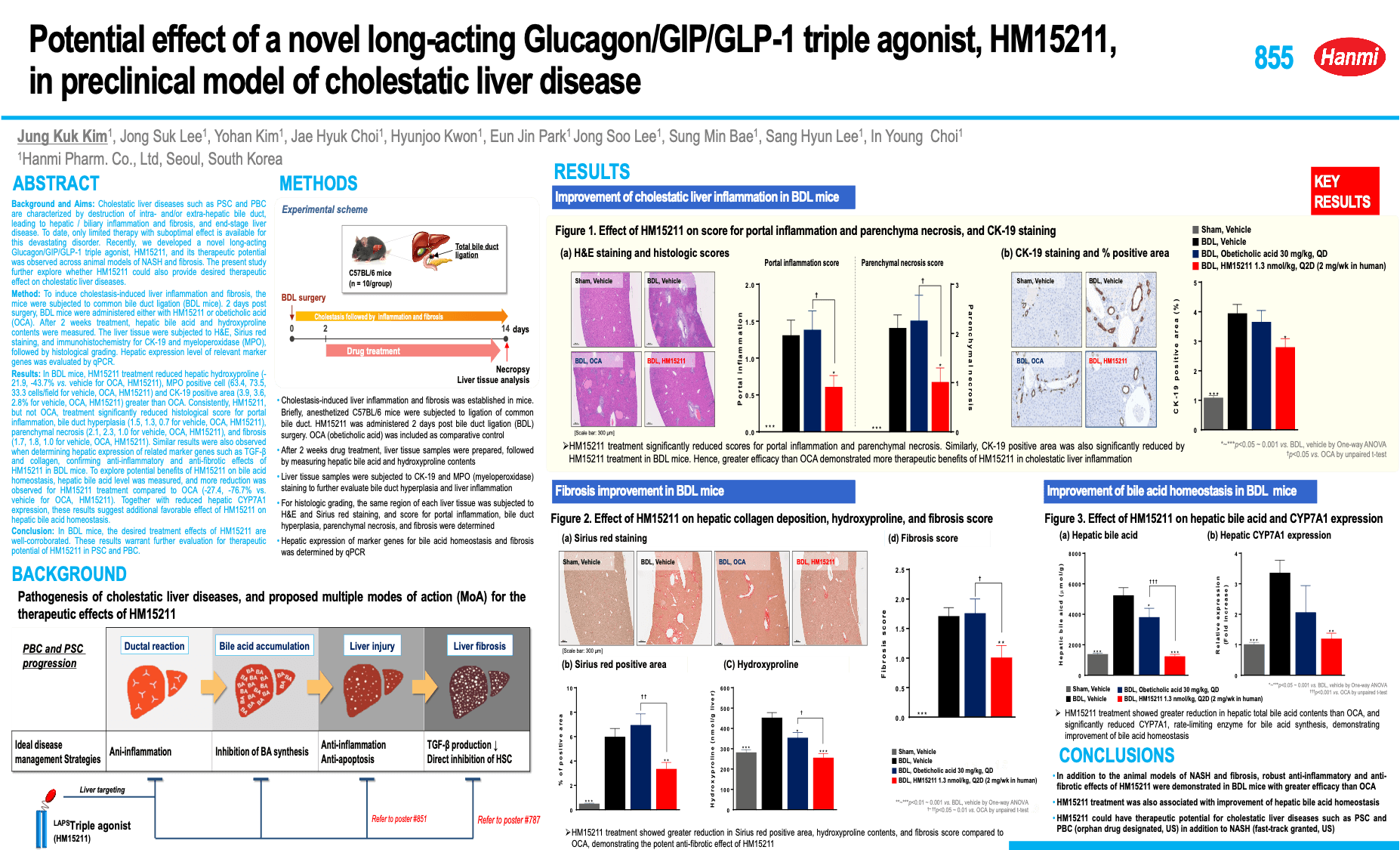
b.[778 - Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of a novel long-acting Glucagon/GIP/GLP-1 triple agonist, HM15211, in TAA induced mouse model of liver injury and fibrosis (21 Sep 2022)]
Background and aims: HM15211 is a novel long-acting triple agonist consisting of Glucagon/GIP/GLP-1 triple agonist conjugated to human IgG FC fragment via short PEG linker. Previously, therapeutic benefits of HM15211 were demonstrated in diet-induced animal models of NASH and fibrosis. Here, the effects of HM15211 on anti-inflammatory and fibrosis (anti-inflammatory and-fibrotic effects of HM15211) were further evaluated in TAA (thioacetamide)-induced liver injury and fibrosis mouse, and underlying mechanism was investigated.
Materials and methods: To induce liver injury and fibrosis, TAA was injected to mouse for 12 weeks with gradual dose increment and HM15211 was administered during last 10 weeks. After the treatment of drug, hepatic hydroxyproline, Sirius red positive area and fibrosis score were determined, and blood level of pro-inflammatory cytokines was measured by using multiplex cytokine analysis. In addition, blood liver enzyme level and hepatic gene expression for fibrosis and inflammation were analysed. To unveil the underlying MoAs, mechanistic study was performed in THP-1 and LX2 cells.
Results: In TAA mice, HM15211 treatment significantly reduced the hepatic hydroxyproline (-51% vs. vehicle, p<0.01), Sirius red positive area (-65% vs. vehicle, p<0.001), and fibrosis score (0.7 for HM15211 vs. 3.0 for vehicle, p<0.001). Considering a baseline fibrosis score of TAA mice at week 2 (1.0), HM15211 treatment could confer both potential reversal effect on pre-existing fibrosis and prevention effect on fibrogenesis. Consistently, expression of hepatic marker genes for fibrosis (i.e. collagen-1α1) and inflammation (i.e. F4/80, TNF-α) were significantly attenuated by HM15211 treatment. Furthermore, multiplex cytokine analysis revealed that HM15211 treatment was associated with robust reduction across blood pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Profound reduction in blood level of liver enzymes was also confirmed. Mechanistically, PMA/LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion of THP-1 cells (human monocytes) was significantly attenuated by HM15211, and TGF-β-induced collagen production was also significantly reduced in LX2 cells (human hepatic stellate cells).
Conclusion: HM15211 effectively improved liver inflammation and fibrosis in TAA mice, and related mechanism was elaborated by in vitro studies. Thus, HM15211 could be a novel therapeutic option for fibrosis caused by NASH. Human study is ongoing to assess the clinical relevance of these promising results.
c.[Anti-fibrotic potential of a novel long-acting Glucagon/GIP/GLP-1 triple agonist (HM15211) in preclinical models of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (21 Sep 2022)]
Background and aims: IPF is an irreversible and progressive pulmonary disorder of unknown causes in which scarring of lung tissue eventually leads to death. A large number of studies have demonstrated that the core mechanisms of fibrosis across various organs are similar. Previously, excellent preclinical efficacy of HM15211, a novel long-acting Glucagon/GIP/GLP-1 triple agonist, on liver fibrosis was confirmed. Since the major distributed tissues of HM15211 were found to be in liver and lung, such findings prompted us to hypothesize that HM15211 could be also a promising drug candidate for IPF, In the present study, its effect on pulmonary function and mortality was evaluated in BLM-induced mouse model of IPF.
Materials and methods: To investigate the therapeutic effect of HM15211 on IPF-induced pulmonary function impairment as well as mortality, BLM induced mouse model of lung fibrosis was established. Briefly, at day 0, 1.5 U/kg and 2.5U/kg of BLM were intratracheally injected to impair pulmonary function and to increase mortality, respectively. HM15211 treatment was initiated from day 7, and continued until day 14 ~ day 21, followed by monitoring the saturation of peripheral oxygen(SpO2) and survival rate. To highlight the therapeutic benefits of HM15211, pirfenidone(PIRF) and nintedanib(NINT) treated groups were included as comparative control.
Results: In 1.5 U/kg BLM mice, markedly impaired lung function was observed at day 7 as indicated by SpO2 (84.0 vs. 95.6% for normal), which was further exacerbated until day 14 (77.1% vs. 96.0% for normal). Interestingly, while PIRF (81.9%) and NINT (81.3%), FDA-approved drugs for IPF management, prevented additional lung function impairment without statistical significance, HM15211 treatment significantly restored the impaired lung function closed to normal level at day 14 (91.5%, p<0.001 vs. BLM, vehicle), demonstrating HM15211’s disease modifying potential. In addition, at 21 days after 2.5 U/kg BLM treatment, substantial decline in survival rate (17%) was effectively inhibited by HM15211, NINT, and PIRF. Notably, HM15211 (61%, p<0.05 vs. BLM, vehicle) showed improved survival rate compared to NINT (33%, no significant) and PIRF (28%, no significant), suggesting potential superiority of HM15211 over current IPF drugs.
Conclusion: HM15211 could possess therapeutic potential for IPF with improved treatment effects over current standard of care. On-going mechanistic studies will elucidate the underlying mode of actions, and human study should be followed up (required) to assess the clinical relevance of these findings.
4. Poster
5. Clinical Trials

- IPF는 임상 1상 준비중
- IPF에 대해 Orphan drug designation
6. 한미 기술
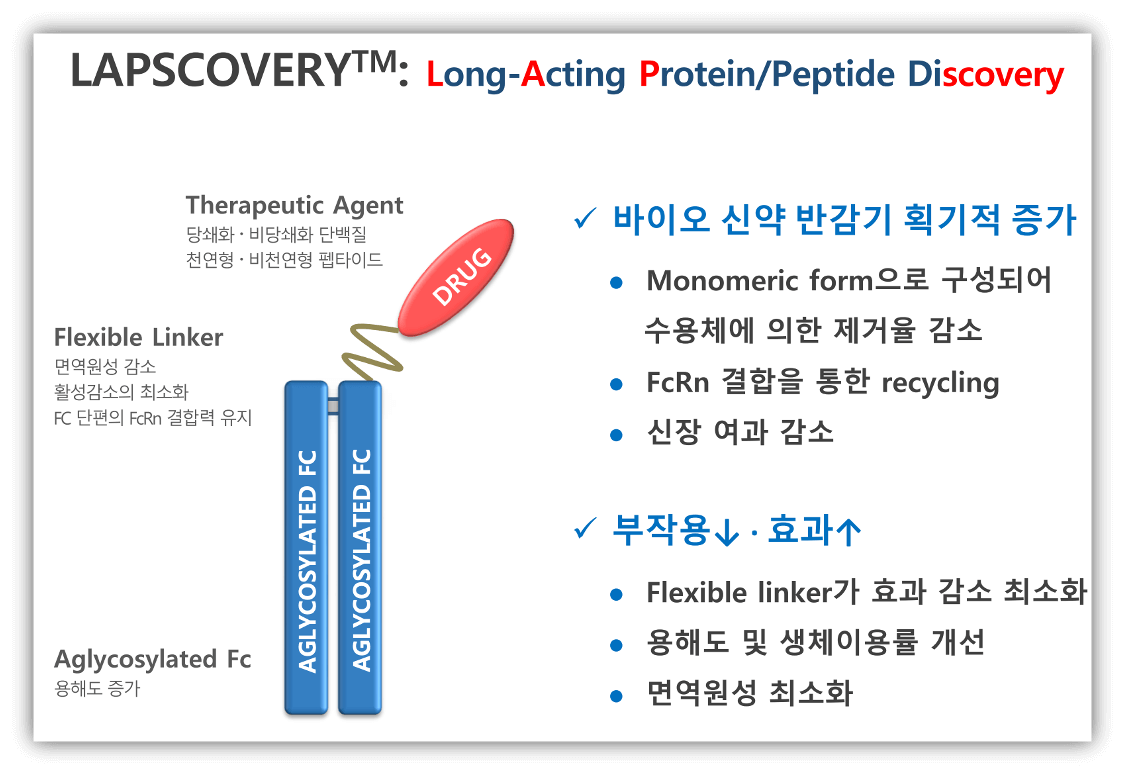
1) 플랫폼 기술 (LAPSCOVERY-Long-acting protein/peptide discovery)
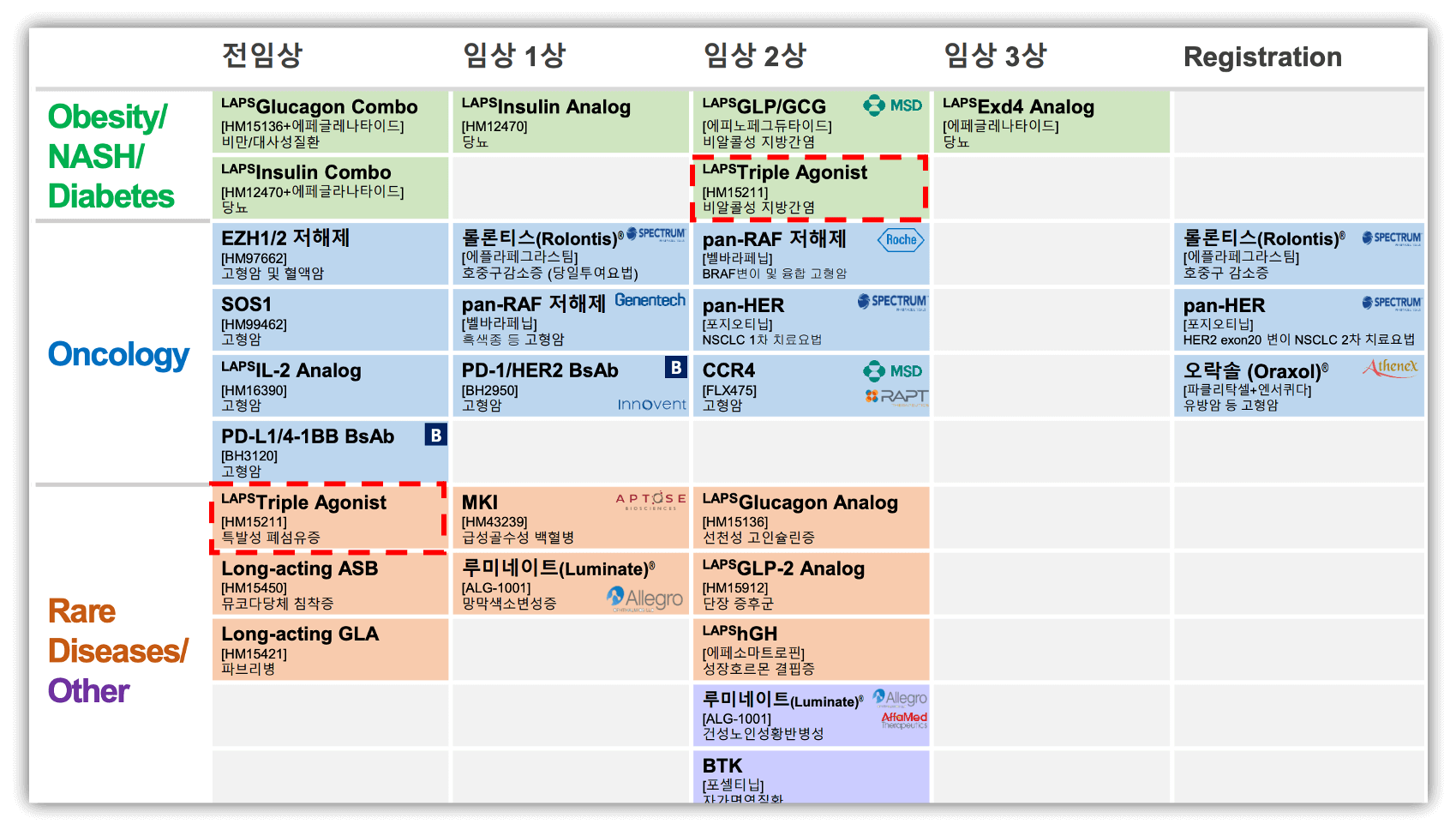
7. 한미 Pipeline
2022.09.20 - [심각한_질병이야기/Respiratory disorder] - 대웅제약 DWN1208 [국내 IPF 치료 약물 개발 1]
대웅제약 DWN1208 [국내 IPF 치료 약물 개발 1]
현재 Idiopathy pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)에 관한 약물은 Pirfenidone과 Nintedanib밖에 없는 상황입니다. 하지만 pirfenidone은 3개 임상 3상을 통해 mortality 개선 효과를 봤지만, 위장관 부작용이 퍼페니돈 사..
scilancer.tistory.com
2022.09.21 - [심각한_질병이야기/Respiratory disorder] - 브릿지바이오 BBT-877 [국내 IPF 치료 약물 개발 2]
2022.09.22 - [심각한_질병이야기/Respiratory disorder] - 나이벡 NIPEP-PF(NP-201)[국내 IPF 치료 약물 개발 3]
'심각한_질병이야기 > Respiratory disorder' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 키트루다(Keytruda)의 수술 전·후 요법이 비소세포폐암(NSCLC) 환자의 무사건 생존 기간을 개선 (0) | 2023.06.13 |
|---|---|
| 나이벡 NIPEP-PF(NP-201)[국내 IPF 치료 약물 개발 3] (0) | 2022.09.22 |
| 닌테다닙(Nintedanib) 개발 상황 리뷰 (0) | 2022.09.22 |
| 브릿지바이오 BBT-877 [국내 IPF 치료 약물 개발 2] (0) | 2022.09.21 |
| 대웅제약 DWN1208 [국내 IPF 치료 약물 개발 1] (0) | 2022.09.20 |